cs231A Homework-4: Image Segmentation
2. Image Segmentation
本节主要实现两个经典的分割方法
- k-means
- meanshift
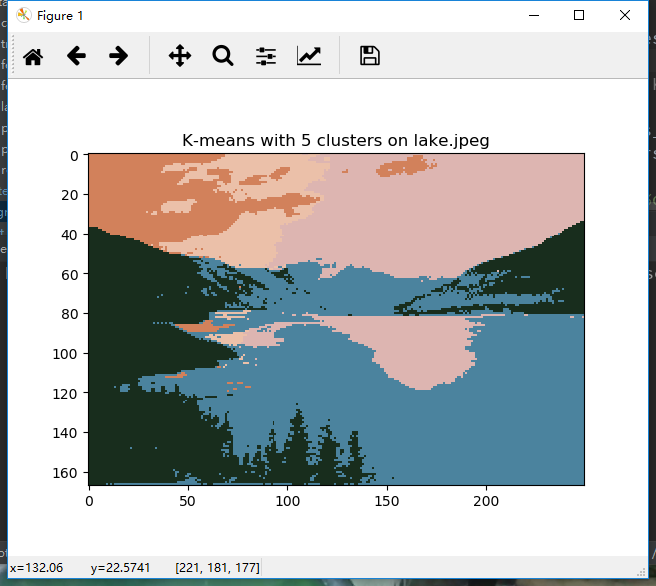
2.1 k-means
函数:kmeans_segmentation(im, features, num_clusters)
参数:
- im: 图片(H,W,3)
- features: 每个像素点的特征(#pixels, M), #pixels为(H,W),特征为[row,col, R,G,B]
- num_clusters: 聚类数量
返回值:
- pixel_cluster: (H,W)矩阵,每个像素点属于的cluster
实现:
- 随机选择num_clusters个中心
- 重复下面步骤直到收敛:
- 将每个像素点归到最近的像素中心点
- 计算每个集合的特征的均值中心
- 直到每个集合的中心不再发生变化
def kmeans_segmentation(im, features, num_clusters):
H, W = im.shape[0], im.shape[1]
N = features.shape[0]
# 第一步: 随机选择num_clusters个种子
center_idx = np.random.randint(N, size=num_clusters)
centriods = features[center_idx]
matrixes = np.zeros((H, W))
# 第二步: 迭代器划分
while True:
# 每个像素到cneter的距离
dist = np.zeros((N, num_clusters))
for i in range(num_clusters):
dist[:, i] = np.linalg.norm(features - centriods[i, :], axis=1) # 距离
# 寻找最近中心
nearest = np.argmin(dist, axis=1) # (N,1)
# 更新
prev_centriods = centriods
for i in range(num_clusters):
pixels_idx = np.where(nearest == i) # 和 第 i 个中心邻近的像素集合
cluster = features[pixels_idx] # (M,5)
centriods[i, :] = np.mean(cluster, axis=0) # 重新计算平均值
# 收敛
if np.array_equal(prev_centriods, centriods):
break
pixels_clusters = np.reshape(nearest, (H, W))
return pixels_clusters
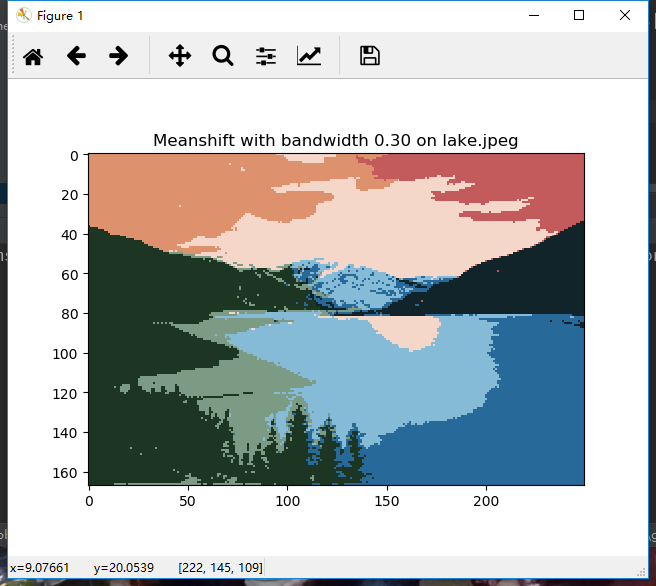
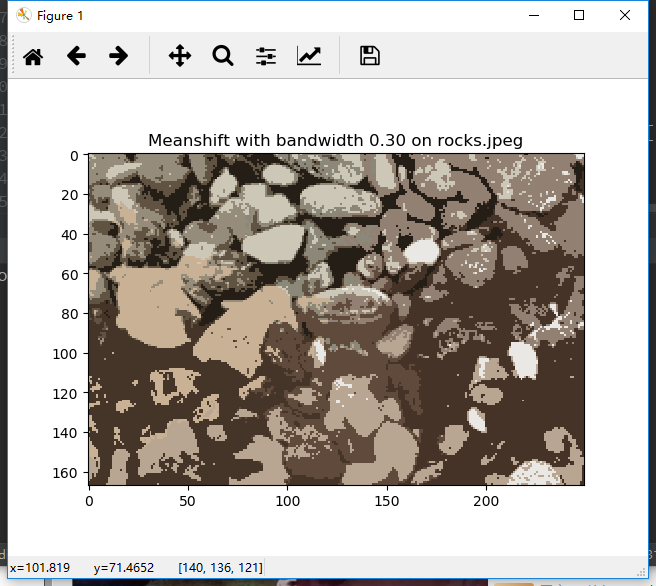
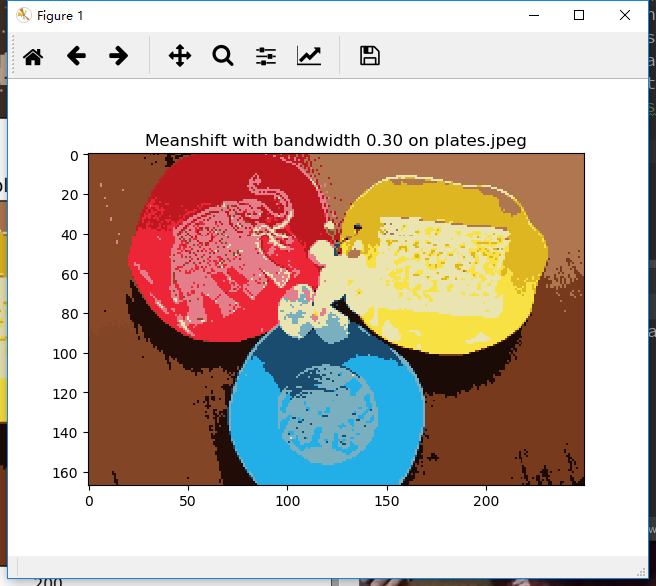
2.2 meanshift
函数: meanshift_segmentation(im, features, bandwidth)
参数:
- im: 图片
- features: 如上
- bandwidth: 均值计算半径
返回值:
- pixel_cluster: H*W 矩阵
实现:
- 随机选择一个未遍历过的像素
- 重新计算均值直到变化不超过1%,将 bandwidth 内的像素点归到当前cluster
- 如果当前cluster漂移,和另一个clouster中心近于半个 bandwidth, 将两个归于一个cluster
- 否则,创建一个新的cluster
def meanshift_segmentation(im, features, bandwidth):
H, W = im.shape[0], im.shape[1]
N, M = features.shape # 数量, 特征维度
mask = np.ones(N)
clusters = []
while np.sum(mask) > 0 : # 当前还有像素未被遍历
loc = np.argwhere(mask > 0)
idx = loc[int(np.random.choice(loc.shape[0], 1)[0])][0] # 随扈挑选一个像素
mask[idx] = 0 # 标记
current_mean = features[idx]
prev_mean = current_mean
while True:
dist = np.linalg.norm(features - prev_mean, axis=1)
incircle = dist < bandwidth # 距离小于半径的点
mask[incircle] = 0
current_mean = np.mean(features[incircle], axis=0) # 新的中心
# 稳定,收敛
if np.linalg.norm(current_mean - prev_mean) < 0.01 * bandwidth:
break
prev_mean = current_mean
isValid = True
for cluster in clusters:
if np.linalg.norm(cluster - current_mean) < 0.5 * bandwidth: # 两个划分为一个cluster
isValid = False
if isValid: # 添加一个新cluster
clusters.append(current_mean)
pixels_clusters = np.zeros((H, W))
clusters = np.array(clusters)
for i in range(N): # 计算每个像素点的最近中心
idx = np.argmin(np.linalg.norm(features[i, :] - clusters, axis=1))
h = int(i/W)
w = i % W
pixels_clusters[h, w] = idx
return pixels_clusters.astype(int)
2.3 结果
k-means
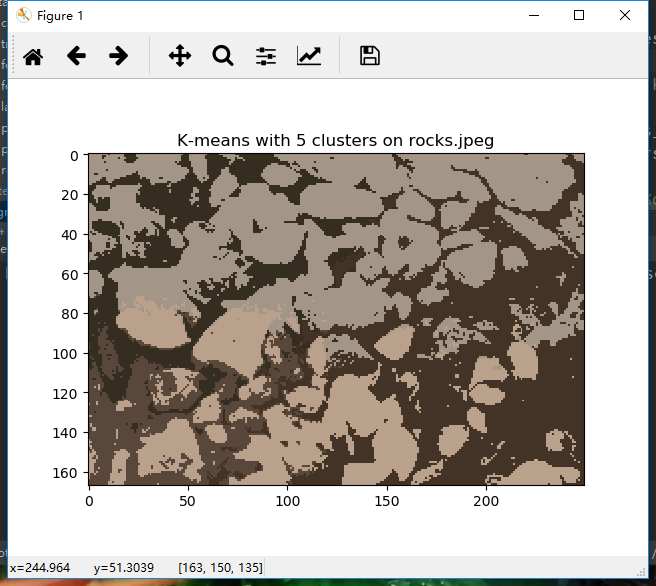
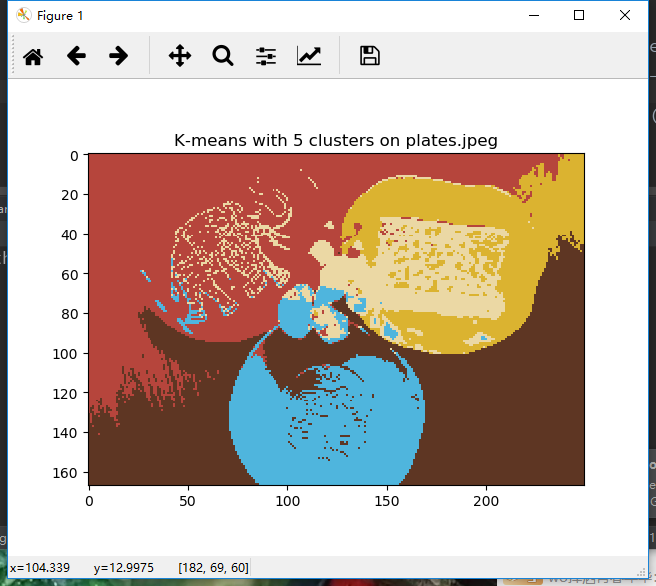
meanshift